Sinus Lifting: Procedure Details, Stages, and Types
[price id=”5249″]
Sinus lifting is a dental procedure often necessary for dental implantation. The specialist introduces materials into the maxillary sinuses to thicken the bone. This straightforward surgical intervention uses local anesthesia and does not take much time.
Reasons for Bone Degradation
Sinus lifting is prescribed for patients who have experienced jawbone atrophy. Signs of this include narrowing and lowering of the bone tissues. Bone degradation occurs within a few months. Thus, the longer the time after tooth extraction, the more likely it is that implants cannot be placed without augmentation.
Examining the anatomical structure of the jaw, one can see that the tooth is located in the alveolar process of the jaw. Due to periodontitis, periodontal diseases, and other dental diseases, bone destruction and structural changes occur. After tooth loss, the height and volume of the bone change. In this place, with prolonged absence of load on the bone, it begins to thin. Its volume narrows with decreased nourishment and blood supply. Therefore, it is advisable to consult dentists for dental implant placement immediately after tooth loss, otherwise, a sinus lifting procedure will be necessary.
Who and When Needs a Sinus Lifting Procedure?
Above, in the lateral areas of the jaw when implantation is needed, there may be difficulties since, physiologically, in most cases, the tooth root is connected to the maxillary sinus. Often there is not enough bone tissue height to place an implant.
If a standard implant is placed without bone grafting, there is a risk of damaging the maxillary sinus. Part of the implant may touch the maxillary cavity located above. This is an unpleasant and dangerous situation, which can lead to the development of sinusitis (chronic inflammation).
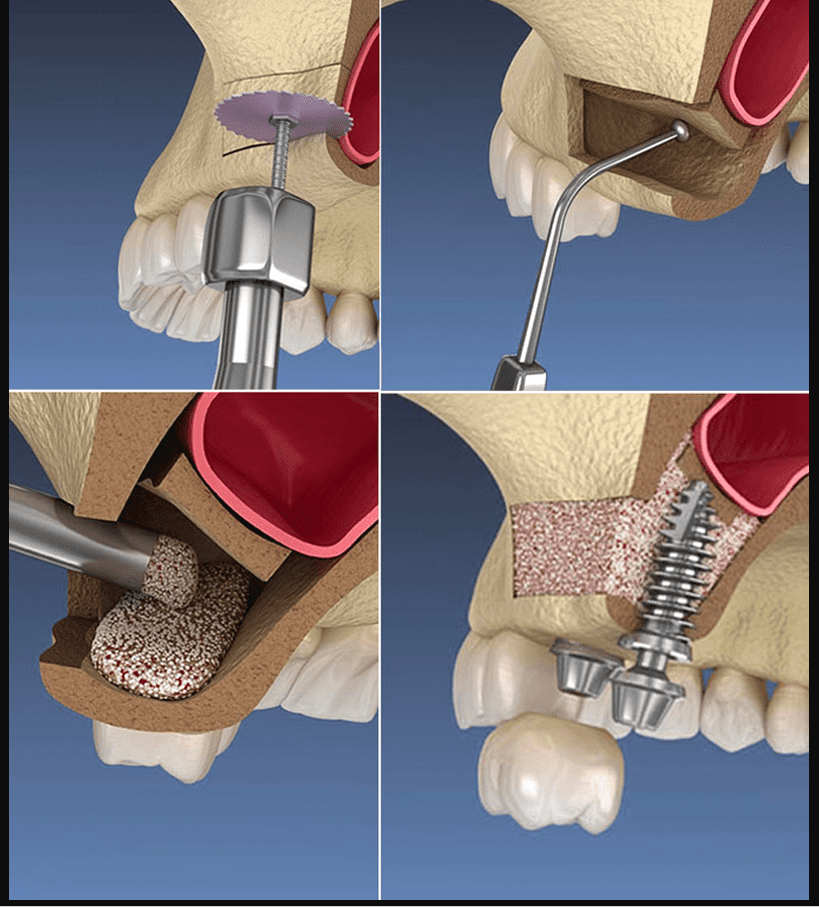
To prevent this situation, doctors separate the lining of the maxillary sinus from the bone and fill it with a special substitute. This is the essence of the sinus lifting procedure. Therefore, specialists lift the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinus and introduce bone material in this place. After six months, it transforms into a dense base for the implant. Only then can a dental implant be placed at this location. However, there are cases when the sinus lifting and implantation procedures are performed simultaneously.
Preparation for Sinus Lifting
Before starting the procedure, the doctor invites the patient for a detailed examination:
- Identification of all inflammatory processes;
- Conducting an anatomical examination;
- Determining the level of jawbone tissue height.
Subsequent pre-operative preparation consists of several stages:
- Examination stage using computed tomography, which creates a 3D model of the jaw. At this stage, the entire sinus is studied internally, a virtual sinus lifting project is created, and the necessary volume of bone material for the operation is determined.
- Laboratory work stage. After studying the computer plan, the doctor creates a template with guide systems for implants.
Pain Relief and Sedation Features
For osteoplasty, pain relief involves applying an analgesic at the end of the upper dental row. Under anesthesia, nerve fibers are blocked, and pain sensations completely disappear for 1-2 hours.
An alternative option is sedation, which is safer for anxious and emotionally distressed patients.
Types and Stages of the Sinus Lifting Procedure
Currently, there are two techniques for performing sinus lifting – open and closed:
- Open involves cutting into the gums on the side and drilling to create a hole in the bone. This allows for adjustments to the shapes of the maxillary sinus by introducing bone material. After closing the hole with a membrane, the opening is sutured. This procedure is recommended when the thickness of the alveolar process is 4-5 millimeters. It is advisable to visit the doctor a week later to remove the stitches. Then, wait another three to four months to install implants.
- The closed method is considered more comfortable. The surgeon makes a hole in the dental socket and immediately introduces bone-grafting paste. This procedure allows for the immediate placement of implants.
- A subtype of the closed procedure is the balloon technique. The floor of the maxillary sinus is altered by conducting a catheter, through which saline is delivered directly into the cavity. This method ensures an even shift and reduces the risks of perforating the maxillary cavity. The closed method can be applied when the thickness of the alveolar process is from 5 millimeters. In this case, the bone tissue can only be increased by 4 millimeters, no more. The duration of the operation is 30 minutes. The mucous membrane fully recovers within seven days, and complete bone regeneration occurs within six months.
Features of the Rehabilitation Period
For quick and easy recovery after osteoplasty, it is essential to follow all medical prescriptions:
- Do not eat for 2 hours.
- Use cold compresses, applying them to the cheek.
- For 1-2 weeks, avoid lifting heavy weights and strenuous physical activity.
- Do not take a hot bath.
- Adjust your diet. Only consume soft food that is easy to chew and does not irritate the mucous membrane of the oral cavity.
- Do not consume alcoholic beverages.
- Do not skip taking medications prescribed after the procedure.
In case of suture rupture, pain sensations, bleeding, increased body temperature, and other symptoms, contact the surgeon who performed the surgery for further recommendations.
Contraindications
There are patients for whom sinus lifting is prohibited. If identified:
- Sinusitis;
- Sinusitis, malignant tumors;
- Heart failure;
- Chronic pathologies in the exacerbation stage;
- Chronic rhinitis;
- Polyps;
- Respiratory infections;
- Blood diseases.
In some cases, the operation can be performed if the patient’s disease is in the compensation stage.
Cost of Sinus Lifting
The price of the sinus lifting procedure depends on several factors: the type of material and its total quantity, the complexity of the operation, and the parameters of the cavity. Only after a full examination can the doctor announce the exact cost of the operation. This indicator is always individual. Therefore, any previously mentioned figure will be conditional.


